Product Description
Product Description
| Material | Aluminium Alloy,Carbon Steel,Stainless steel,Copper,Brass,Nylon,Plastic(Customized Material) |
| Producing Equipment | 3 Axis,4 Axis,5 Axis CNC Machines,Automatic Lathe Machines,Stamping Machines,CNC Milling machines,CNC Turning Machines,Turning Milling Compound Machines,Grinding Machines,Rolling Machines,Laser Machines. |
| Surface Treatment | Anodizing,Polishing,Electroplating,Heat Treatment,Spray Paint,Sand Blasting. |
| Testing Equipment | Salt Spray Test, Hardness Tester, Coating Thickness Tester, Two Dimensions Measuring Instrument. |
| Quality Testing | 100% Quality Inspection Before Shipment. |
| Lead Time | Generally, The Delivery Date Is 7-15 Days,Delivery Time of Bulk Order Is More Than 15 days. |
| Tolerance and Roughness | Size Tolerance:+/-0.005 – 0.01mm,Roughness: Ra0.2 – Ra3.2 (Custom Size Requirements) |
| Cargo Shipment | Express(DHL,Fedex,UPS, TNT ),Air shipment+Local Express Delivery,Ocean Shipment. |
| Main Markets | America, Europe, Australia, Asia. |
| Payment Type | T/T, L/C, Paypal,Western Union,Others. |
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
HangZhou Fuyouda Technology Co., Ltd. Was established in city known as the “world factory”-HangZhou. We are factory and have many kinds of machine, such as 5-axis CNC machines, lath machines, turning milling compound machines. After 10 years of R&D, production and sales, we have 80% market share in the field of 3D printer parts in China and we are specializing in CNC machinig for 10 years. We are committed to creating a work and production environment that is above the industry average. We adopt scientific production management methods to improve production efficiency and reduce production costs. Please believe and choose us! We adhere to the management principles of “Quality First, Customer first and Credit-based” since the establishment of the company and always do our best to satisfy potential needs of our customers. Our company is sincerely willing to cooperate with enterprises from all over the world in order to realize a CZPT situation since the trend of economic globalization has developed with anirresistible force.
Our Advantages
FAQ
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
|---|---|
| Color: | Customized |
| Customized: | Customized |
| Standard: | International |
| Type: | Connection |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 3.8/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can you provide examples of machinery that use helical gears?
Helical gears are widely used in various types of machinery and mechanical systems. Their unique tooth geometry and smooth operation make them suitable for applications that require high torque transmission, precision, and low noise levels. Here are some examples of machinery and equipment that commonly utilize helical gears:
- Industrial Gearboxes: Helical gears are extensively employed in industrial gearboxes used in various industries such as manufacturing, mining, oil and gas, and power generation. These gearboxes are responsible for transmitting power and adjusting rotational speed in large machinery and equipment, including conveyors, mixers, crushers, extruders, and heavy-duty pumps.
- Automotive Transmissions: Helical gears play a crucial role in automotive transmissions, both manual and automatic. They facilitate the smooth shifting of gears and the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. Helical gears are commonly found in the main transmission system, differential gears, and gear sets used in the gearbox.
- Machine Tools: Many types of machine tools, such as milling machines, lathes, and grinding machines, rely on helical gears for precise motion control and power transmission. Helical gears are used in the spindle drives, feed mechanisms, and gearboxes of these machines, enabling accurate and efficient metal shaping, cutting, and finishing operations.
- Rotary Compressors: Helical gears are employed in rotary compressors, which are widely used in industries such as refrigeration, HVAC, and pneumatic systems. The helical gears in these compressors help to compress and transfer gases or fluids, generating the desired pressure and flow rates.
- Printing Presses: High-speed printing presses utilize helical gears in their drive systems. The gears enable the precise synchronization of various components, such as rollers, cylinders, and plate cylinders, ensuring accurate paper feeding, ink distribution, and image transfer during the printing process.
- Paper and Pulp Industry: Helical gears are utilized in machinery used in the paper and pulp industry, including paper mills and paperboard manufacturing plants. They are employed in equipment such as pulpers, refiners, stock pumps, and paper machine drives, facilitating the processing, refining, and transportation of pulp and paper materials.
- Construction Equipment: Helical gears are found in various construction machinery, such as cranes, excavators, loaders, and bulldozers. They are used in the drivetrains, swing mechanisms, and hydraulic systems of these machines, providing the necessary torque, speed control, and power transmission capabilities.
- Marine Propulsion Systems: Helical gears are utilized in marine propulsion systems, including marine engines, outboard motors, and ship propulsion systems. They enable efficient power transmission from the engine to the propeller, ensuring smooth and reliable operation of watercraft.
- Wind Turbines: In wind energy applications, helical gears are commonly used in wind turbine gearboxes. They help convert the low-speed rotation of the turbine blades into higher rotational speeds required by the electrical generators, enabling efficient energy generation from wind power.
- Food Processing Machinery: Helical gears find applications in the food processing industry, where they are used in equipment such as mixers, conveyors, extruders, and packaging machines. They facilitate the movement of ingredients, blending, and precise control of processing parameters.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and widespread use of helical gears across various industries and applications. The unique characteristics of helical gears make them suitable for a wide range of machinery that requires smooth, efficient, and reliable power transmission.
How do you retrofit an existing mechanical system with helical gears?
Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with helical gears involves replacing the current gear system with helical gears to improve performance, efficiency, or address specific requirements. The process requires careful planning, analysis, and implementation to ensure a successful retrofit. Here is a detailed explanation of how to retrofit an existing mechanical system with helical gears:
- Assess the Existing System: Begin by thoroughly assessing the existing mechanical system. Understand its design, operating conditions, gear specifications, and performance limitations. Identify the reasons for retrofitting, such as the need for increased load capacity, improved efficiency, noise reduction, or other specific requirements.
- Define Retrofit Objectives: Clearly define the objectives of the retrofit. Determine the specific improvements or modifications desired from the retrofit. This could include increasing torque capacity, reducing backlash, improving gear meshing characteristics, or optimizing gear ratios. Having well-defined objectives will guide the retrofitting process.
- Perform Gear Design and Analysis: Based on the defined objectives, conduct gear design and analysis to determine the appropriate helical gear configuration. Consider factors such as gear size, tooth profile, helix angle, module or diametral pitch, and gear material. Use engineering calculations, software simulations, or consult with gear design experts to ensure the selected helical gears meet the retrofit objectives and are compatible with the existing system.
- Modify Gear Housing and Mounting: In some cases, retrofitting with helical gears may require modifications to the gear housing or mounting arrangements. Ensure that the gear housing can accommodate the helical gears and provide proper alignment and support. Modify or adapt the housing as necessary to ensure a precise fit and alignment of the new gear system.
- Manufacture or Source Helical Gears: Once the gear design is finalized, manufacture or source the helical gears according to the specifications determined during the design phase. Work with experienced gear manufacturers or suppliers who can provide high-quality helical gears that meet the required specifications and performance criteria.
- Installation and Alignment: Remove the existing gears and install the helical gears in the mechanical system. Ensure proper alignment of the gears to maintain smooth operation and minimize wear. Follow recommended installation procedures and torque specifications provided by the gear manufacturer. Consider using alignment tools, such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems, to achieve precise gear alignment.
- Test and Fine-tune: After installation, conduct thorough testing of the retrofit system. Monitor performance, check for any abnormal vibrations, noise, or operating issues. Fine-tune the system as needed, making adjustments to gear meshing, lubrication, or other parameters to optimize performance and ensure the retrofit objectives are met.
- Monitor and Maintain: Once the retrofit is complete, establish a regular monitoring and maintenance schedule. Periodically inspect the helical gears for wear, perform lubrication checks, and address any maintenance requirements. Regular monitoring and maintenance will help ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the retrofit system.
Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with helical gears can significantly enhance its performance, efficiency, and reliability. However, it is essential to carefully plan and execute the retrofitting process to achieve the desired outcomes. Consulting with gear design experts and experienced professionals can provide valuable guidance and expertise throughout the retrofitting process.
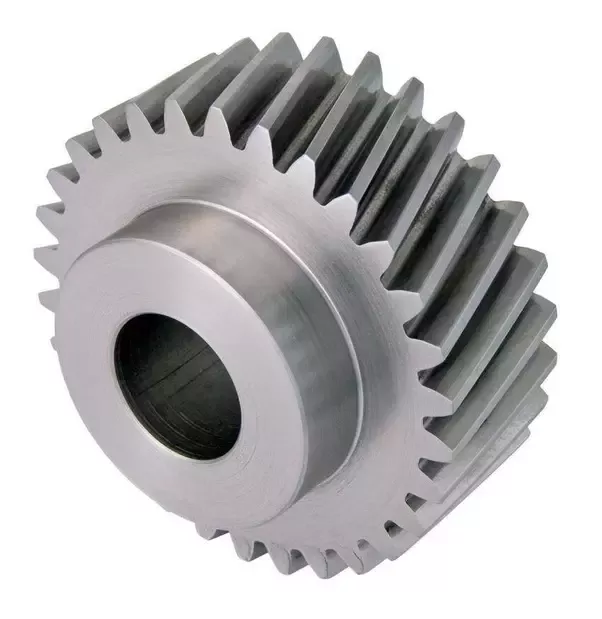

Can you explain the concept of helical gear teeth and their orientation?
The concept of helical gear teeth and their orientation is essential to understanding the design and operation of helical gears. Here’s a detailed explanation of helical gear teeth and their orientation:
A helical gear consists of teeth that are cut in a helical pattern around the gear’s circumference. Unlike spur gears, which have teeth that are perpendicular to the gear axis, helical gears have teeth that are angled or inclined with respect to the gear axis. This inclination gives the teeth a helix shape, resulting in the name “helical” gears.
The orientation of helical gear teeth is defined by two main parameters:
- Helix Angle: The helix angle represents the angle formed between the tooth surface and an imaginary line perpendicular to the gear axis. It determines the degree of inclination or spiral of the gear teeth. The helix angle is typically measured in degrees. Positive helix angles indicate a right-hand helix, where the teeth slope in a right-hand direction when viewed from the gear’s end. Negative helix angles represent a left-hand helix, where the teeth slope in a left-hand direction. The helix angle affects the gear’s performance characteristics, including tooth engagement, load distribution, and axial thrust.
- Lead Angle: The lead angle is the angle formed by the helical tooth and a plane perpendicular to the gear axis. It represents the angle of advance of the helix over one revolution of the gear. The lead angle is equal to the helix angle divided by the gear’s number of teeth. It is commonly used to define the helical gear’s size and pitch.
The helical tooth orientation offers several advantages over spur gears:
- Smooth and Quiet Operation: The helical shape of the teeth allows for gradual engagement and disengagement during gear rotation. This results in smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears, which often produce noise due to the sudden contact between teeth.
- Increased Load-Carrying Capacity: The helical tooth design provides a larger contact area between meshing gears compared to spur gears. This increased contact area allows helical gears to transmit higher loads and handle greater torque without excessive wear or tooth failure.
- Load Distribution: The helical orientation of the teeth enables load distribution along the tooth face. Multiple teeth are engaged simultaneously, distributing the load across a broader surface area. This characteristic helps minimize stress concentrations and increases the gear’s durability.
- Axial Thrust Load: The helical tooth engagement introduces axial forces and thrust loads along the gear axis. These forces must be properly supported and managed in the gear system design to ensure smooth operation and prevent excessive wear or failure.
The design and manufacturing of helical gears require specialized cutting tools and machining processes. The helical teeth are typically generated using gear hobbing or gear shaping methods. The tooth profile is carefully designed to ensure proper meshing and minimize noise, vibration, and wear.
In summary, helical gear teeth have a helical or spiral shape, which distinguishes them from the perpendicular teeth of spur gears. The orientation of helical gear teeth is defined by the helix angle and lead angle. Helical gears offer advantages such as smooth operation, increased load-carrying capacity, load distribution, and axial thrust load. These characteristics make helical gears suitable for applications that require efficient power transmission, precise motion control, and reduced noise and vibration.


editor by CX 2023-09-11